The Company recognizes our response to climate change as an important management issue. For key issues related to sustainability including our response to climate change, the Sustainability Committee chaired by an Executive Officer prepares guidelines and plans and promotes initiatives to achieve our targets.
We have created an appropriate oversight structure through the Board of Directors in which the details evaluated at the Sustainability Committee are deliberated and reported as necessary at Board of Directors meetings.
In the Construction Supply Division that is the covered business, we have a system in which those responsible for promoting and those in charge of sustainability (including climate change) are placed at covered units and we reflect climate change-related points in business strategy and business promotion.
|
Meeting bodies and other systems |
Roles and responsibilities |
|
Board of Directors |
Oversight of climate change response |
|
Sustainability Committee |
Preparing guidelines and plans related to sustainability including climate change response, deciding important items, and promoting initiatives for key issues |
The world is experiencing constant damage from abnormal weather, and if sufficient measures are not taken, that damage will further intensify, and there is the risk of damage on a global scale. Given these conditions, the Paris Agreement that took effect in 2016 established long-term targets to limit the average rise in global temperature to well below 2°C compared to pre-industrial levels and to make every effort to limit it to 1.5°C. As the world begins to take action to realize the scenario of a less than 2°C increase in global temperature, the Company sees this move as both a risk and as an opportunity, and the Sustainability Committee is evaluating and preparing indicators to act as concrete behavioral guidelines and targets.
To realize a sustainable society, the Company has identified key issues that are highly important to the Company, its stakeholders, and society to pursue both sustainable growth and enhancement of our corporate value. While confirming the state of progress for our targets to respond to these key issues, we are working to create solutions through our business activities.
We perform sequential scenario analysis and impact evaluation of business fields judged to have a strong impact on our business.
We use the results of this scenario analysis to formulate both response plans and behavioral guidelines.
Our main business, the construction supply business in Japan (made up 59.2% of sales in FY2020 results)
Percentage of sales of each business division (%)
Composition of the covered business
|
Segment |
Field |
Main products and services |
|
Housing |
Energy solutions |
Solar energy systems, storage batteries |
|
Insulation materials |
Insulation materials |
|
|
Housing materials |
Cladding, housing and facility equipment, interior materials |
|
|
Non-housing |
Construction materials |
Cladding, foundation pillars, foundation improvement construction methods, fire-resistant coverings |
To predict an uncertain future, it is necessary to select and set multiple temperature band scenarios including the less than 2°C scenario.
To do so, the Company has referenced information from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and the International Energy Agency (IEA) and has selected two scenarios, the 2°C scenario (RCP 2.6: Scenario 1) and the 4°C scenario (RCP 8.5: Scenario 2).
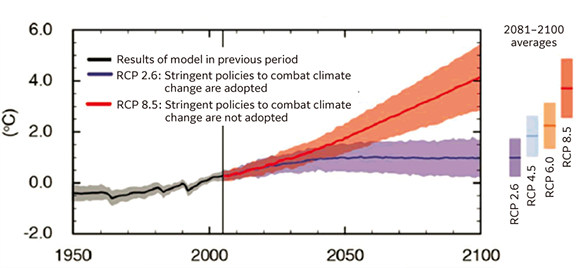
- 拡大
- Source: Environmental Innovation Center
(IPCC 5th Assessment Report partially modified)
|
2°C scenario (RCP 2.6: Scenario 1) |
|
|
4°C scenario (RCP 8.5: Scenario 2) |
|
Based on the above predictions, at the Sustainability Committee, risk and opportunity analysis for each of the covered units in the construction supply business in Japan is performed, shared, and used in medium- to long-term forecasting and in future business strategy.
|
2°C scenario (RCP 2.6: Scenario 1) Changes in markets |
|
|
4°C scenario |
|
In the scenarios defined in the scenario groups (world view of the 2°C and 4°C scenarios), the specific risks and opportunities envisioned are as follows.
|
Risk category |
Evaluation targets of risks |
Expected time period of occurrence |
Impact |
|
|
Transition risk |
Policy and regulatory risk |
Increased costs from the introduction and strengthening of systems related to regulations on GHG emission reduction |
Medium term |
Large |
|
Risk of slower growth in market scale due to reduced prices of feed-in tariffs for electricity and subsidies |
Medium term |
Medium |
||
|
Technological risk |
Reduced competitiveness of existing products with the popularization of low-carbon technology with stronger regulations |
Long term |
Medium |
|
|
Market risk |
Lower margins from price pass-through by suppliers |
Long term |
Large |
|
|
Reputation risk |
Risk that investors and financial institutions will judge that information disclosure is insufficient, causing negative effects on financing |
Medium term |
Large |
|
|
Physical risk |
Acute risk |
Supply cutoffs from disasters at suppliers caused by the normalization of abnormal weather |
Medium term |
Large |
|
Chronic risk |
Deteriorating work environments and productivity and delays in construction completion at construction sites caused by rising temperatures |
Long term |
Medium |
|
|
Opportunity category |
Evaluation targets of opportunities |
Expected time period of occurrence |
Impact |
|
Opportunities related to resource efficiency |
Increasing needs for lighter, alternative materials as steel prices rise |
Medium term |
Large |
|
Opportunities related to energy sources |
Expansion of the renewable energy market by setting long-term CO_{2} reduction targets |
Medium term |
Medium |
|
Opportunities related to products and services |
Providing new solutions by developing and partnering with new business partners (installation and processing) |
Medium term |
Small |
|
New business development through development and partnerships with new suppliers |
Medium term |
Medium |
|
|
Creation of new businesses with expanded products and services that contribute to an appropriate response to climate change |
Long term |
Large |
|
|
Market-related opportunities |
Expanded business through portfolio shifts |
Medium term |
Large |
|
Increased demand for highly sustainable products and services |
Medium term |
Large |
The Company aims to expand our solutions and contribute to building a sustainable society in the three fields of “energy saving,” “weight saving,” and “labor saving” identified as focus fields in our “DANTOTSU Strategy [Becoming our customers’ best of the best]” put forth in the “Sustainability X (Cross)” section of our medium-term management plan announced in 2020.
|
Energy saving |
Expanding solutions that pursue effective energy use in buildings, starting with the insulation filed and energy solutions field |
|
Labor saving |
Providing optimal solutions in terms of quality, ease of installation, and work environments |
The Takashima Group is addressing the risk of climate change, which it regards as one of its key risks. To address risks and opportunities associated with climate change, the Takashima Group has established a working group, which enlists the involvement of Sustainability Committee members. The working group has been performing scenario analysis based on the TCFD recommendations, identifying key risks and opportunities, and evaluating the degree of impact of such risks and opportunities. Going forward, the Sustainability Committee will persist with initiatives that involve analyzing risks, formulating countermeasures, and conducting progress management. Currently, the Company is building an environment-related risk management framework as part of its Company-wide risk management structure. We will proceed in addressing climate change risks by coordinating efforts of the Environmental Management Committee, Sustainability Committee, and Risk Management Committee, while also having the Company implement and enhance the effectiveness of comprehensive risk management. Going forward, we will continue to enhance our systems for evaluating and addressing climate change risks.
The Company started calculating Scope 1 and 2 greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in FY2021. The scope of these calculations will be progressively expanded to take into account resources and other factors.
With respect to Scope 3 emissions, the Company builds overall systems associated with the supply chain and accordingly recognizes that its social responsibility entails promoting carbon neutrality throughout the supply chain in serving as a value-adding trading company that provides necessary functions and solutions.
This time, as part of the sustainability road map for which the groundwork has been made, we have set a target for the rate of reduction of GHG emissions (Scope 1 and 2) of 35% reduction vs FY2022 for 2030. To achieve targets, we will engage the entire efforts of the Group to continue various measures for reduction.
GHG emissions of the Takashima Group in fiscal 2024 (market-based figures)
|
Scopes 1 and 2 |
Scope 3 |
|
|
Takashima (non-consolidated) |
177.7 (t-CO2) |
– |
|
Domestic group companies |
5,258.1 (t-CO2) |
– |
|
Overseas Group companies |
2,788.6 (t-CO2) |
– |
|
Total |
8,224.4 (t-CO2) |
– |
Domestic group companies
Total for ten domestic subsidiaries (TAKASHIMA INDUSTRIES CO., LTD., Hi-Land Inc., iTak International (Japan) Co., Ltd., TAKCEL Co., Ltd., CLS Corporation, Rest Corporation, New Energy Distribution System Inc., Gansui Corporation, Naruto-SP Industries Co., Ltd., and Sinbou Edix Co., Ltd.)
Does not include Sanwa Holdings Co., Ltd. and its 14 subsidiaries.
Overseas group companies
Total for six iTak group companies (iTak (International) Limited, iTak International (Shenzhen) Limited, iTak International (Shanghai) Limited, iTak International (Vietnam) Co.,Ltd., iTak International (Thailand) Limited, iTak International (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd.)
